[알고리즘] Java로 DFS, BFS구현하기
업데이트:
DFS란?
DFS란 Depth First Search의 약자로 하나의 정점을 깊게 파고들어 탐색하는 방식입니다.
스택을 이용하여 구현할 수 있으며, 재귀 함수의 특징을 통한 구현이 일반적입니다.
BFS란?
BFS란 Breadth First Search의 약자로 DFS처럼 하나의 경로를 깊게 탐색하지 않고 넓게 검사합니다.
큐를 이용하여 구현할 수 있습니다.
구현 전체 코드 (Java)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
/* 인접행렬 그래프 클래스
* nV: 정점. Vertex의 개수
* nE: 간선. Edge의 개수
*/
class AdjGraph{
private int nV;
private int[][] graph;
private boolean[] hasVisited;
//생성자
public AdjGraph(int nV) {
//멤버변수 초기화
this.nV = nV;
this.graph = new int[nV+1][nV+1];
this.hasVisited = new boolean[nV+1];
}
//양방향 간선 추가
public void add(int x, int y) {
graph[x][y] = 1;
graph[y][x] = 1;
}
//단방향 간선 추가
public void addSingle(int x, int y) {
graph[x][y] = 1;
}
//visited 초기화
public void clear() {
for(int i=1; i<=nV; i++) {
hasVisited[i] = false;
}
}
//인접행렬 출력
public void print() {
System.out.println("= 인접행렬 출력 =");
for(int i=0; i<graph.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<graph[i].length; j++)
System.out.print(graph[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
}
//DFS Logic
public void dfs(int idx) {
//dfs()에 들어온 정점을 방문처리한다.
hasVisited[idx] = true;
System.out.print(idx + " ");
/*
* i가 1부터 끝까지 돌며 자신과 연결된 정점을 찾음.
* 정점을 찾았다면 잠시 함수를 멈추고 다음 dfs(i)를 실행했다가 처리가 모두 완료되면 돌아옴.
* 따라서 깊이우선탐색이 가능함.
*/
for(int i=1; i<=nV; i++) {
//연결이 되어있고 해당 정점이 미방문일경우.
if(graph[idx][i] == 1 && hasVisited[i] == false)
dfs(i);
}
}
//BFS Logic
public void bfs(int idx) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// queue에 시작 정점 추가.
queue.add(idx);
hasVisited[idx] = true;
while( !queue.isEmpty() ) {
// poll: pop하고 pop된 값 반환
idx = queue.poll();
System.out.print(idx + " ");
for(int i=1; i<=nV; i++) {
if (graph[idx][i] == 1 && hasVisited[i] == false) {
//queue에 인접 정점 삽입
queue.add(i);
//방문처리
hasVisited[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
// Main이 있는 클래스
public class GraphViewer {
//멤버변수
int nV;
int nE;
AdjGraph graph;
//생성자
public GraphViewer() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//정점의 개수 받기
nV = sc.nextInt();
//간선의 개수 받기
nE = sc.nextInt();
//그래프 초기화
graph = new AdjGraph(nV);
//graph에 간선 추가하기.
for(int i=0; i<nE; i++)
graph.add(sc.nextInt(), sc.nextInt());
//인접행렬 프린트하기
graph.print();
//DFS로 출력
System.out.print("DFS로 정점 1부터 탐색한 결과: ");
graph.dfs(1);
//BFS로 출력. clear로 visited 초기화
graph.clear();
System.out.print("BFS로 정점 1부터 탐색한 결과: ");
graph.bfs(1);
sc.close();
}
//메인 메서드
public static void main(String[] args) {
GraphViewer gv = new GraphViewer();
}
}
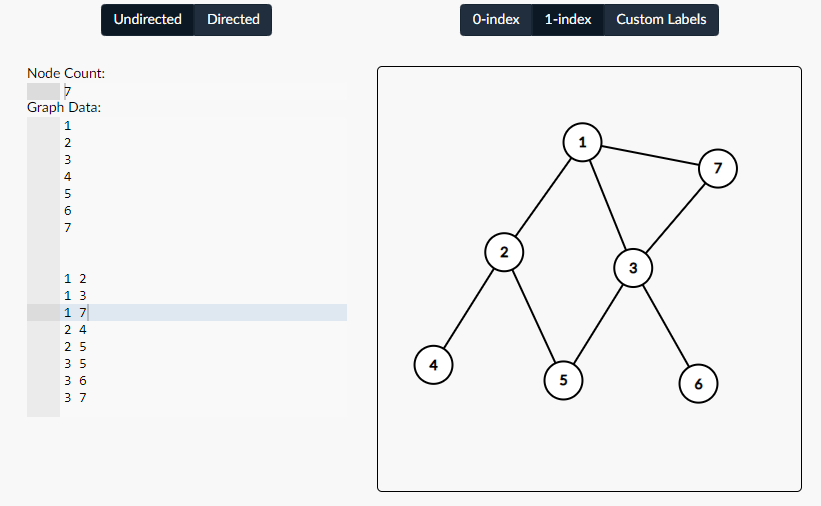
그래프 & 실행 결과

댓글남기기