웹 기술 - CORS
업데이트:
개요
웹 개발을 하다보면 아래와 같은 ‘CORS policy’ 에러에 마주하는 경우가 많다.
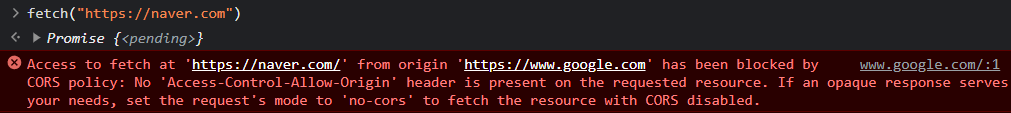
이번 포스트에서는 CORS를 이해하는 것이 목표이다.
Web Origin과 Same Origin Policy
Web Origin과 Same Origin Policy는 국제 인터넷 표준화 기구(IETF)가 관리하는 RFC-6454 (2011.12) 문서에서 등장하는 표현이다.
The Web Origin Concept
This document defines the concept of an “origin”, which is often used as the scope of authority or privilege by user agents. Typically, user agents isolate content retrieved from different origins to prevent malicious web site operators from interfering with the operation of benign web sites. In addition to outlining the principles that underlie the concept of origin, this document details how to determine the origin of a URI and how to serialize an origin into a string. It also defines an HTTP header field, named “Origin”, that indicates which origins are associated with an HTTP request.
… rfc6454 중에서
Principles of the Same-Origin Policy
Many user agents undertake actions on behalf of remote parties. For example, HTTP user agents follow redirects, which are instructions from remote servers, and HTML user agents expose rich Document Object Model (DOM) interfaces to scripts retrieved from remote servers. Without any security model, user agents might undertake actions detrimental to the user or to other parties. Over time, many web- related technologies have converged towards a common security model, known colloquially as the “same-origin policy”. Although this security model evolved largely organically, the same-origin policy can be understood in terms of a handful of key concepts. This section presents those concepts and provides advice about how to use these concepts securely.
… rfc6454 중에서
Same-Origin Policy는 보안을 위한 정책으로 User Agent(=브라우저)는, 같은 Web Origin에 대해서만 통신하게 해야한다는 정책이다.
예를 들자면, 브라우저는 https://wichan7.github.io 에서 https://google.com 으로 XHR 요청하지 못하게 막아야 하는 책임이 있다.
Cross Origin Resource Sharing
SOP가 보안상 중요하기는 했지만, 타도메인의 리소스를 호출하는 것이 유용한 경우가 잦아 CORS라고 부르는 예외 정책이 추가되었다.
CORS는 타도메인(Cross-Origin) 간 리소스를 공유하기 위해 만들어진 정책이다.
CORS 통신의 3가지 시나리오
Simple Requests
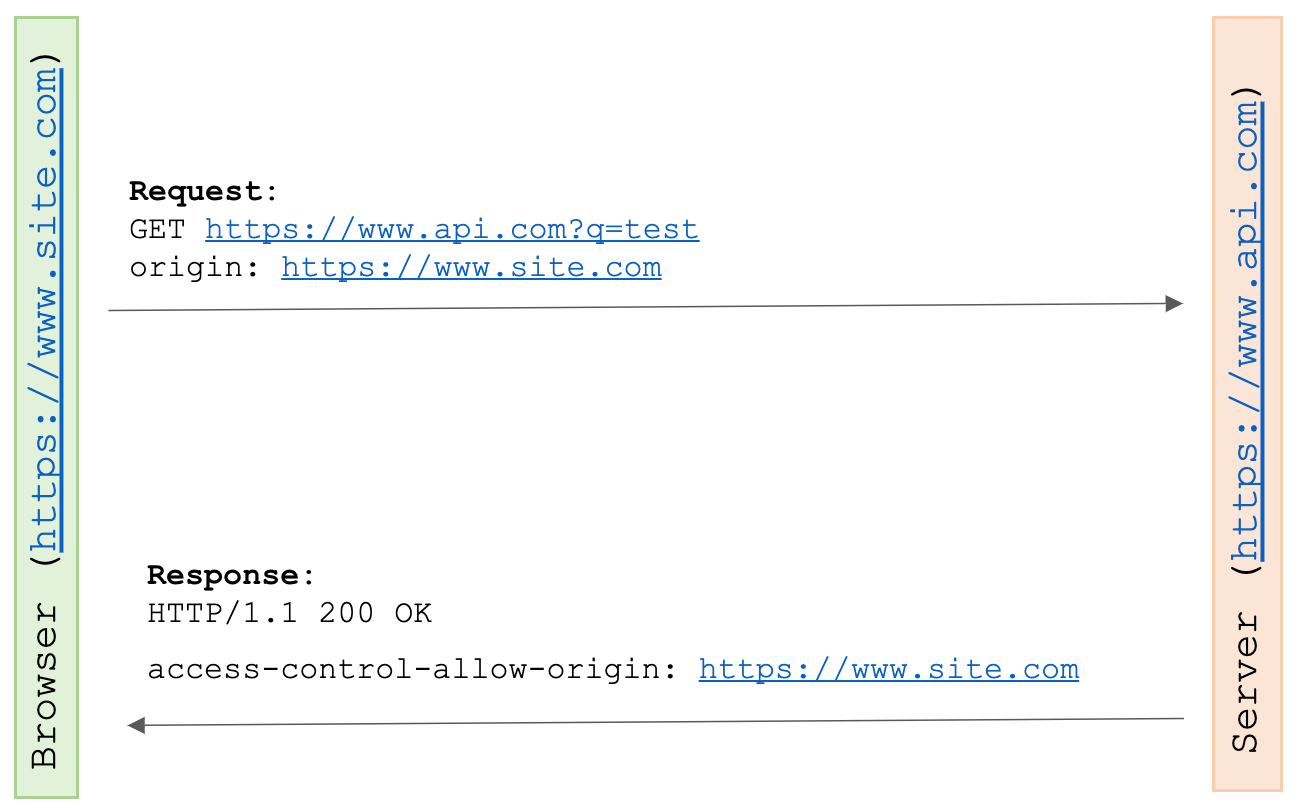
아래 조건을 모두 충족하면, 브라우저는 Simple-Requests로 동작한다.
- GET, HEAD, POST 요청인 경우
- 요청에 Accept, Accept-Language, Content-Language, Content-Type와 같은, 브라우저 헤더만 포함한 경우
- 요청에 CORS Safelisted 헤더만 포함한 경우
- … 기타 등등 (상세는 원본 출처에 있음)
브라우저는 HTTP 요청에 Origin 헤더를 포함해 요청하고, 서버는 응답 access-control-allow-origin 헤더에 SOP 예외 도메인을 포함한다.
브라우저는 Request의 Origin과 access-control-allow-origin을 비교해, 같으면 정상 처리하고 다르면 폐기한다.
Non-Simple Requests
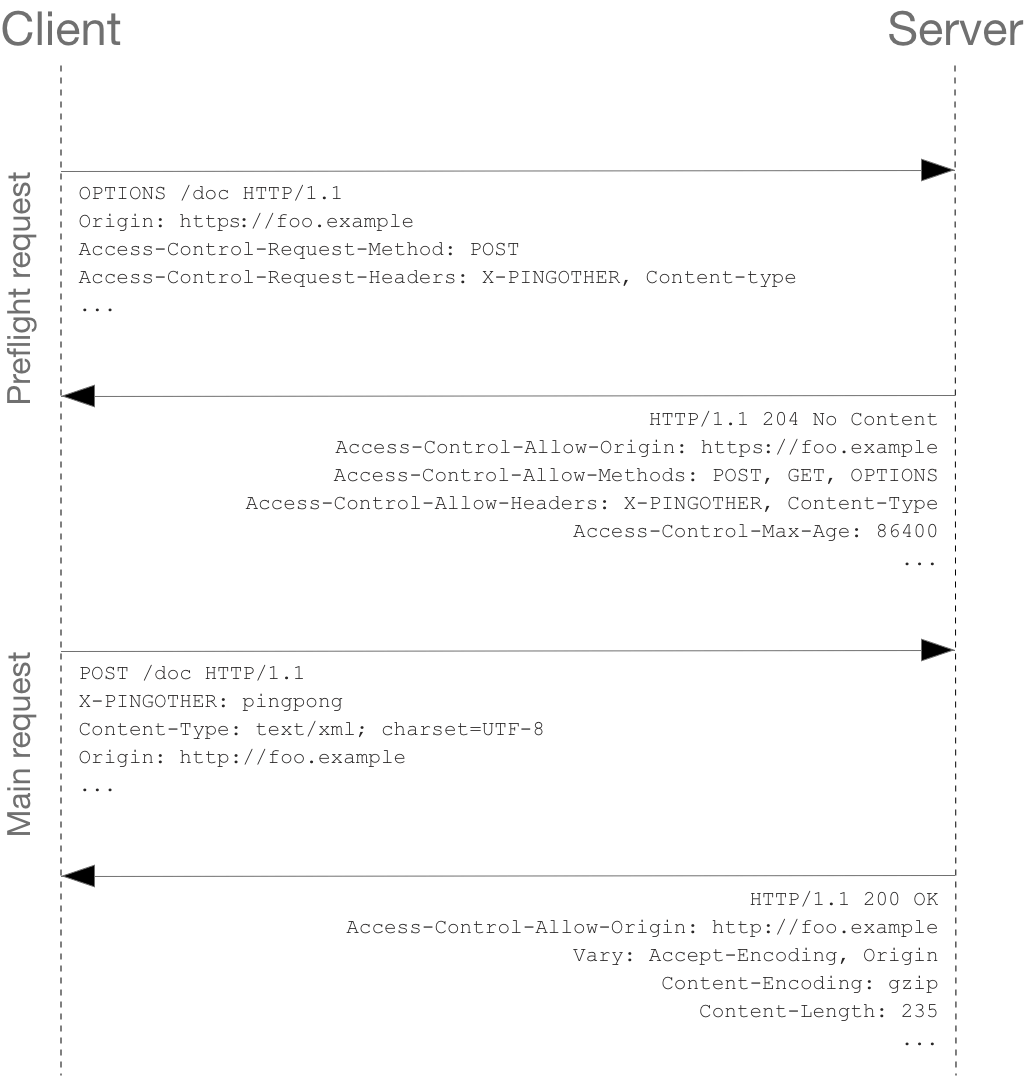
Simple-Requests에 포함되지 않은 요청이면, Pre-flight 요청이라고 부르는 과정이 추가된다.
브라우저는 실제 Request 이전에 access-control-allow-origin을 받아보기 위한 OPTION 요청을 수행한다.
이것이 Pre-flight 요청이다. pre-flight가 정상이면 이후 실제 request를 수행하게 된다.
Credentialed Requests

기본적으로 Cookie나 Authorization 등 인증 정보들을 CORS 하려면, 서버가 access-control-allow-origin만 응답해서는 안된다.
브라우저는 Request시 credentials 옵션을 사용해야 하고, 서버는 access-control-allow-credentials:true 헤더와, 와일드 카드가 아닌 도메인이 명시된 access-control-allow-origin 헤더를 응답해야 한다.
결론
CORS는 브라우저와 서버 간에서 SOP 예외로 통신해야 할 때 필요한 정책이다.
결국 SOP는 브라우저-서버 간 정책이기 때문에, 서버-서버 통신에서는 CORS를 사용하라는 에러 문구가 발생하지 않는다.
자체 서비스라면 프레임워크에서 제공하는 cors 관련 라이브러리를 사용해 처리할 수 있겠고, 타 서비스에 XHR 호출해야하는 경우 Proxy를 구성하는 방법이 있겠다.
댓글남기기